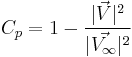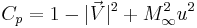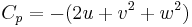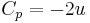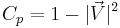Aerodynamic potential flow code
Aerodynamic potential flow or panel codes are used to determine the velocity and subsequently the pressure distribution on an object. This may be a simple two-dimensional object, such as a circle or wing or it may be a three-dimensional vehicle.
A series of sources and doublets are used to model the panels and wakes respectively. These codes may be valid at subsonic and supersonic speeds.
History
Early panel codes were developed in the late 1960s to early 1970s. Advanced panel codes, such as Panair (developed by Boeing), were first introduced in the late 1970s, and gained popularity as computing speed increased. Over time, panel codes were replaced with higher order panel methods and subsequently CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics). However, panel codes are still used for preliminary aerodynamic analysis as the time required for an analysis run is significantly less due to a decreased number of elements.
Assumptions
These are the various assumptions that go into developing potential flow panel methods:
- Inviscid
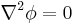
- Incompressible
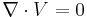
- Irrotational
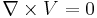
- Steady
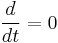
However, the incompressible flow assumption may be removed from the potential flow derivation leaving:
- Potential Flow (inviscid, irrotational, steady)
Derivation of Panel Method Solution to Potential Flow Problem
- From Small Disturbances
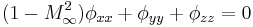 (subsonic)
(subsonic)
- From Divergence Theorem
- Let Velocity U be a twice continuously differentiable function in a region of volume V in space. This function is the stream function
 .
. - Let P be a point in the volume V
- Let S be the surface boundary of the volume V.
- Let Q be a point on the surface S, and
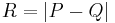 .
.
As Q goes from inside V to the surface of V,
- Therefore:
For :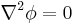 , where the surface normal points inwards.
, where the surface normal points inwards.
This equation can be broken down into the a both a source term and a doublet term.
The Source Strength at an arbitrary point Q is:
The Doublet Strength at an arbitrary point Q is:
The simplified potential flow equation is:
With this equation, along with applicable boundary conditions, the potential flow problem may be solved.
Required Boundary Conditions
The velocity potential on the internal surface and all points inside V (or on the lower surface S) is 0.
The Doublet Strength is:
The velocity potential on the outer surface is normal to the surface and is equal to the freestream velocity.
These basic equations are satisfied when the geometry is a 'watertight' geometry. If it is watertight, it is a well-posed problem. If it is not, it is an ill-posed problem.
Discretization of Potential Flow Equation
The potential flow equation with well-posed boundary conditions applied is:
- Note that the
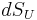 integration term is evaluated only on the upper surface, while th
integration term is evaluated only on the upper surface, while th 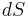 integral term is evaluated on the upper and lower surfaces.
integral term is evaluated on the upper and lower surfaces.
The continuous surface S may now be discretized into discrete panels. These panels will approximate the shape of the actual surface. This value of the various source and doublet terms may be evaluated at a convenient point (such as the centroid of the panel). Some assumed distribution of the source and doublet strengths (typically constant or linear) are used at points other than the centroid. A single source term s of unknown strength 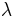 and a single doublet term m of unknown strength
and a single doublet term m of unknown strength 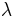 are defined at a given point.
are defined at a given point.
where:
These terms can be used to create a system of linear equations which can be solved for all the unknown values of 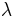 .
.
Methods for Discretizing Panels
- constant strength - simple, large number of panels required
- linear varying strength - reasonable answer, little difficulty in creating well-posed problems
- quadratic varying strength - accurate, more difficult to create a well-posed problem
Some techniques are commonly used to model surfaces.[1]
- Body Thickness by line sources
- Body Lift by line doublets
- Wing Thickness by constant source panels
- Wing Lift by constant pressure panels
- Wing-Body Interface by constant pressure panels
Methods of determining pressure
Once the Velocity at every point is determined, the pressure can be determined by using one of the following formulas. All various Pressure coefficient methods produce results that are similar and are commonly used to identify regions where the results are invalid.
Pressure Coefficient is defined as:
The Isentropic Pressure Coefficient is:
The Incompressible Pressure Coefficient is:
The Second Order Pressure Coefficient is:
The Slender Body Theory Pressure Coefficient is:
The Linear Theory Pressure Coefficient is:
The Reduced Second Order Pressure Coefficient is:
What Panel Methods Can't Do
- Panel methods are inviscid solutions. You will not capture viscous effects except via user “modeling” by changing the geometry.
- Solutions are invalid as soon as the flow develops local supersonic zones (Critical Mach Number)
Commonly used potential flow codes
- PanAir a502 (created by Boeing)
- HESS (created by Douglas)
- MACAERO (created by McDonnell Aircraft)
- PMARC (created by NASA)
- Quadpan (created by Lockheed)
- LinAir (created by Desktop Aeronautics)
- VSAero
- CMARC (created by AeroLogic, Personal Simulation Works, based in PMARC)
- DesignFOIL (created by DreeseCode Software LLC)
See also
- Aerodynamics Small Disturbances
- Stream function
- Conformal mapping
- Velocity potential
- Divergence theorem
- Joukowsky transform
- Potential flow
- Circulation
- Biot-Savart law
Notes
- ^ Section 7.6
References
- Public Domain Aerodynamic Software, A Panair Distribution Source, Ralph Carmichael
- Panair Volume I, Theory Manual, Version 3.0, Michael Epton, Alfred Magnus, 1990 Boeing
- Panair Volume II, Theory Manual, Version 3.0, Michael Epton, Alfred Magnus, 1990 Boeing
- Panair Volume III, Case Manual, Version 1.0, Michael Epton, Kenneth Sidewell, Alfred Magnus, 1981 Boeing
- Panair Volume IV, Maintenance Document, Version 3.0, Michael Epton, Kenneth Sidewell, Alfred Magnus, 1991 Boeing
- Recent Experience in Using Finite Element Methods For The Solution Of Problems In Aerodynamic Intereference, Ralph Carmichael, 1971 NASA Ames Research Center
- [1]
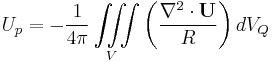
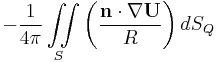
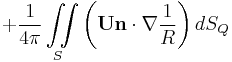
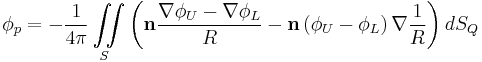
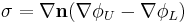
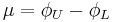
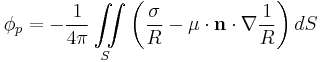
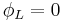
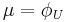
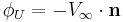
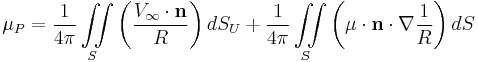
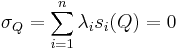
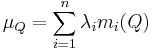
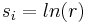
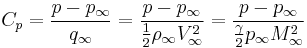
![C_p = \frac{2} {\gamma M_\infty^2} \left( \left(1%2B\frac{\gamma-1} {2} M_\infty^2 \left[\frac{1-|\vec{V}|^2}{|\vec{V_\infty}|^2}\right]\right)^{ \frac{\gamma}{\gamma-1} } -1 \right)](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/c4ea62d1b1a4525d408242ceff7490ca.png)